Break Even Analysis
Break-even analysis refers to the point at which total costs and total revenue are equal. A break-even point analysis is used to determine the number of units or dollars of revenue needed to cover total costs. Break-even analysis is important to business owners and managers in determining how many units (or revenues) are needed to cover the total cost of the business. Breakeven analysis is commonly applied in make-or-buy decisions.
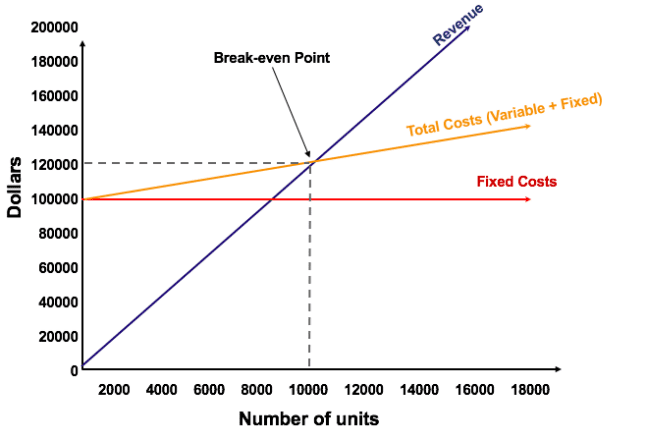
Key aspects:
- To find the cut-off production volume from where a firm will make a profit.
- Breakeven is the intersection point of total sales revenue and total cost lines on a graph as shown in the figure above.
- Breakeven is related to sensitivity analysis, but in sensitivity analysis, the variable of interest is allowed to vary.
- Breakeven Point in Units (QBE) = FC / (r – v),
where FC is fixed cost,
r is revenue per unit, and
v is variable cost per unit. - Profit = Revenue – Total Cost.
- Average Cost Per Unit (Cu) = (FC/Q) + v.
Project Selection Criteria:
- Single Project: The acceptance criterion is to accept the project if the estimated quantity exceeds the breakeven quantity.
- Two Alternatives: It determines the value of a parameter that is common to both alternatives. The selection guideline is to select the alternative with the lower variable cost if the estimated quantity exceeds the breakeven amount. If the anticipated level of the common variable is below the breakeven value, select the alternative with the higher variable cost.

